- dermatophytes;
- Yeast-like fungi of the genus Candida;
- Mold.
route of infection
- Direct contact with an infected person. Here, the fungus moves from its habitat into healthy areas, causing infection;
- Family way. In this case, the infection occurs while using the patient's personal belongings: shoes, personal hygiene products, etc.
risk factors
- diabetes;
- Varicose veins;
- Injury to nails and adjacent tissues;
- HIV and other immunodeficiency diseases;
- long-term antibiotic use;
- weakened immune system;
- Vascular and skin disorders, dermatitis, diaper rash;
- Disturbances in the blood supply to the limbs;
- Not enough hygiene.
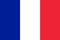
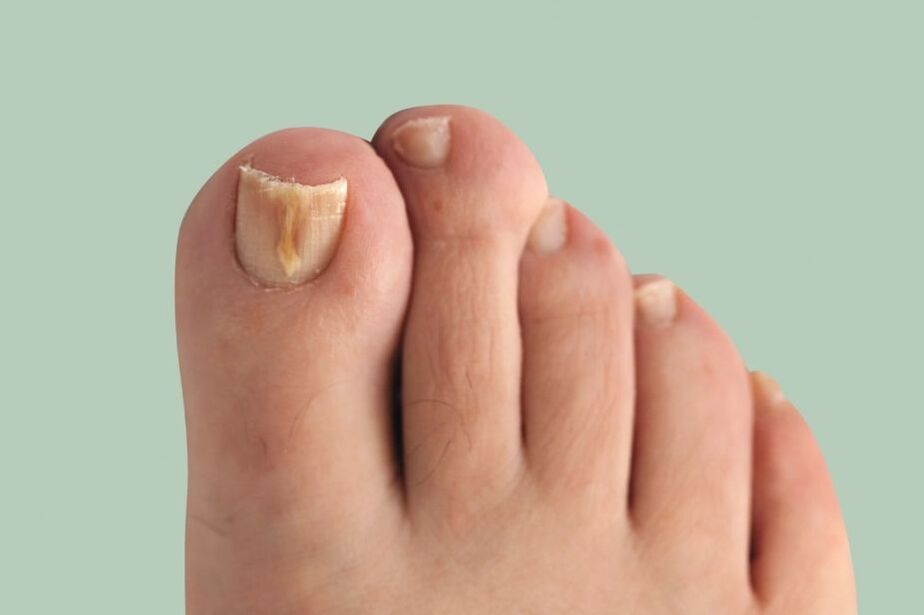
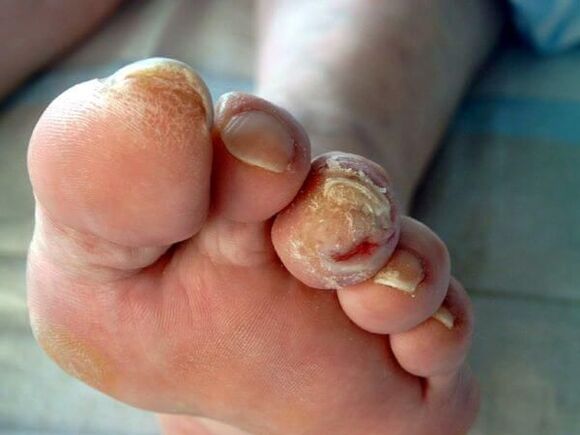
Symptoms of onychomycosis (onychomycosis)
- Pigmentation abnormalities - nail color changes to yellow, black, green, gray or brown (the type of color depends on the type of fungus);
- Onycholysis – Separation of the nail plate from the nail bed;
- changes in nail plate thickness;
- hapalonychia - reduction in the thickness of the plates and their softening;
- Onychomycosis - Nails that appear concave and teaspoon-shaped;
- Hyperonychia - thickening of the nail plate and hypertrophy of the nails;
- Onychomycosis - The nail plate is thickened, discolored, and curved like a beak;
- Changes in nail bed thickness (hyperkeratosis - nail bed thickening);
- Changes in the surface of the nail plate: pits, grooves, ridges;
- Changes in the nail fold and surrounding skin (paronychia - inflammation of the proximal nail fold).
The pathogenesis of onychomycosis (onychomycosis)
Classification and stages of onychomycosis (onychomycosis)
- distal subungual;
- Surface white;
- proximal subungual;
- Total malnutrition.
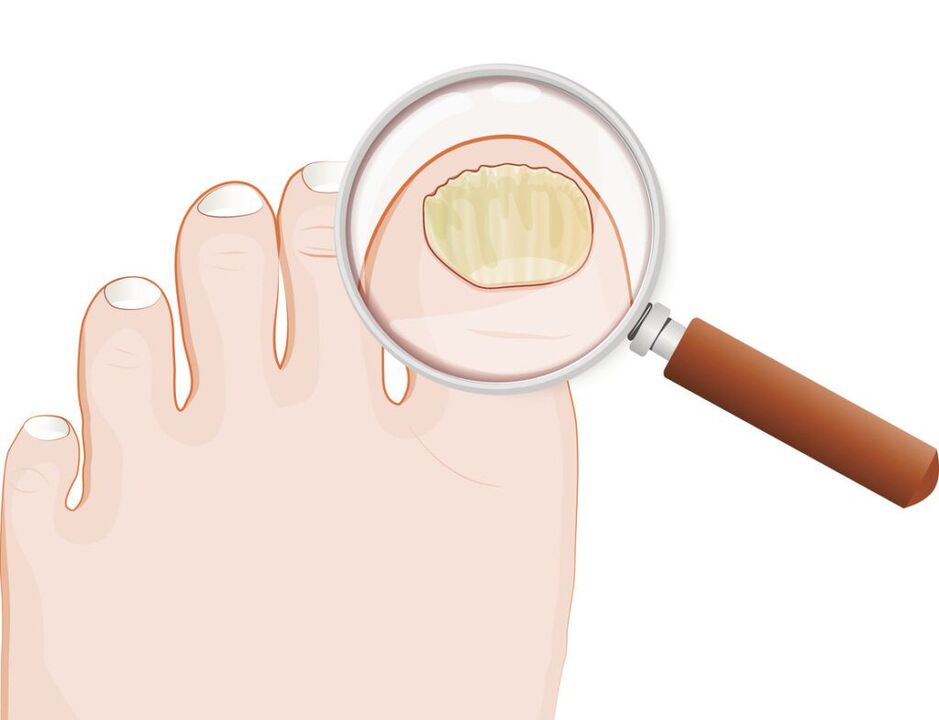
- Nutritionally normal: There are light yellow and light white stripes in the nail thickness, but the shape of the nail plate does not change, and there is no subungual hyperkeratosis;
- Hypertrophic type:The nail plate turns yellow, becomes thickened and brittle due to subungual hyperkeratosis, and has jagged edges;
- Malnutrition:As voids form, the nail plate thins and detaches from the nail bed.
Complications of Onychomycosis (Onychomycosis)
Diagnosis of Onychomycosis (Onychomycosis)
- surface morphology- Scrape off the nail plate;
- remote mode- Need to scrape the nail bed and a deck;
- proximal subungual morphology- Use a drill to collect material, or perform a nail biopsy, or scrape it from the nail bed.
- A biological sample of the affected tissue is cultured. To do this, it is placed in an artificial nutrient medium, in which the pathogen is cultured to determine its type;
- The polymerase chain reaction (PCR) method detects pathogen DNA in samples of affected tissue.
When to see a doctor
getting ready to see a doctor
Treat onychomycosis (onychomycosis)
- Topical treatment.
- Systemic treatment.
- Combination therapy.
- Corrective treatment.
- There are limited forms of damage to the nail plate (according to KIOTOS).
- There are contraindications for systemic use: allergies, liver disease, renal insufficiency, pregnancy, lactation.
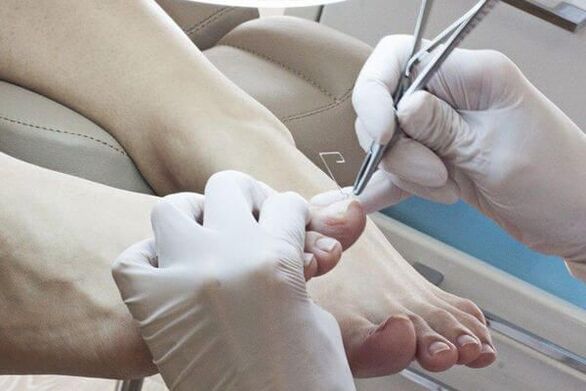
- Use a file, pliers or drill for mechanical removal.
- Use cuticle patches. Before applying a keratolysis plaster, seal the skin around the nail with a plaster, apply a patch of plaster (urea with salicylic acid) on top and seal with tape. Plaster blocks are replaced every 2-3 days. After each removal, the affected portion of the nail is mechanically removed.
- surgical. The procedure is very painful and traumatic because when the nail plate is removed, the growth zone may be damaged, causing the deformed nail to regrow.
- Apply to nails: varnish;
- Suitable for rollers: creams, ointments, solutions.
- Common forms of deck damage.
- Topical treatments lack effectiveness (i. e. , healthy nails do not grow back after 6 months of treatment for onychomycosis on hands and 9-12 months of treatment for onychomycosis on feet).
- Antifungals - have antifungal effects;
- Antiseptic - has antifungal and antibacterial properties. They are rarely used only when other antifungals are not available;
- Multi-Ingredient – In addition to antifungals, they also contain other medications such as anti-inflammatory drugs.
- Standard—take medication every day for the prescribed treatment period;
- Shortening - the treatment period is shortened and can be carried out at the regular dose or at an increased dose;
- Intermittent - treatment is divided into several short sessions with intervals equal to the duration of the sessions;
- Pulse therapy - treatment is divided into several short sessions, with intervals between sessions that are longer than the duration of the session.
- Triazoles;
- Allylamine;
- Others (third generation drugs).
home remedies
- iodine. Before use, feet must be steamed dry, washed with laundry soap, and the affected nail plate area removed. Next, treat the nails and the skin between the fingers with iodine, soak them in the soda solution for 20-30 minutes and dry thoroughly;
- vinegar. 1 tablespoon for 3 liters of water. apple cider vinegar and add a little potassium permanganate. Soak your feet in the bathtub for 20-30 minutes, then dry them thoroughly;
- hydrogen peroxide. After thoroughly steaming your feet, remove the affected nail plate area. Place a cotton pad soaked in hydrogen peroxide over it, wrap it with a bandage, and leave it for half an hour.
Myths and Dangerous Misconceptions about Treating Onychomycosis
forecast. prevention
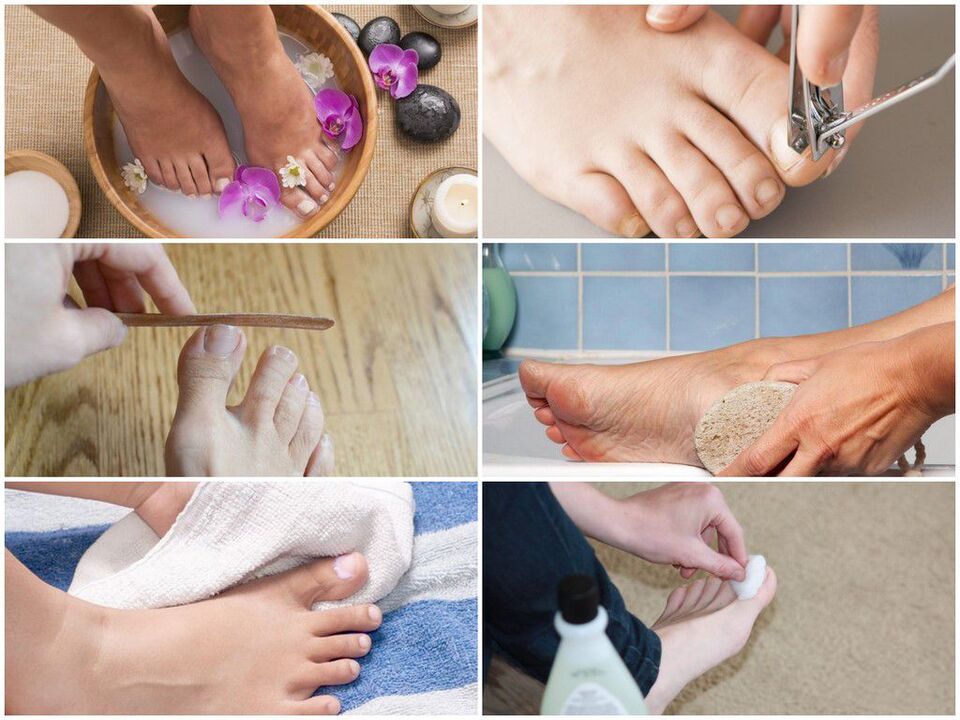
- Try to wear comfortable, high-quality shoes (to prevent your feet from sweating excessively);
- It is recommended to change socks and tights every day;
- Only use separate shoes. For patients being treated for onychomycosis, shoes must be disposed of at the beginning of treatment, throughout treatment, and at least monthly after treatment is completed;
- Use foot antiperspirant if necessary;
- Use personal nail care kit (scissors, files);
- Use antifungal topical preparations (sprays, creams and pencils) before and after going to public places (pools, bathrooms, gyms);
- Identify the source of fungal infections in the home and treat them at the same time.